最近公共祖先(LCA)
信息
此题目来自 洛谷, 原始题目与提交代码请前往 P3379 【模板】最近公共祖先(LCA) - 洛谷。
题目描述
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入格式
第一行包含三个正整数 ,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来 行每行包含两个正整数 ,表示 结点和 结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来 行每行包含两个正整数 ,表示询问 结点和 结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式
输出包含 M 行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
输入输出样例
输入 #1
5 5 4
3 1
2 4
5 1
1 4
2 4
3 2
3 5
1 2
4 5
输出 #1
4
4
1
4
4
说明/提示
对于 的数据,,。
对于 的数据,,。
对于 的数据,,,不保证 。
样例说明:
该树结构如下:
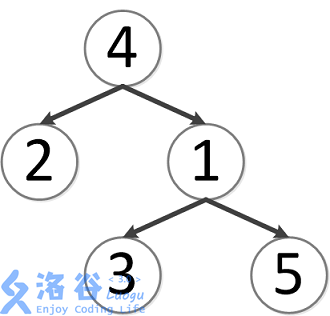
第一次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第二次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第三次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第四次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第五次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
故输出依次为 。
题目解答
- 深度优先搜索算法
- 倍增法
- 树链剖分
- Tarjan 算法
显而易见,我们可以确认树, 之后再从 、 两个结点处上浮, 直到两个结点相同即可。
这种方法的难点是怎么确认树, 我们可以通过 DFS 来搜索每个结点, 确认它们的父结点与深度。 之后判断 、 二者深度是否相同, 不同的话就让更深的结点向上浮; 然后,我们让两个结点一起上浮, 直到两个结点指向同一个结点即可。
我们来处理树:
- C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define repeat(n) for (size_t _ = 0; _ < n; _++)
typedef unsigned int u_int;
using namespace std;
vector<vector<u_int>> tree;
vector<u_int> parent, depth;
u_int N, M, S;
void processTree(u_int __top, u_int __parent, u_int __depth) {
parent[__top - 1] = __parent; // 记录父节点
depth[__top - 1] = __depth; // 记录深度
for (auto& __node : tree[__top - 1]) {
if (__node == __parent) continue; // 避免回环
processTree(__node, __top, __depth + 1); // 递归处理子节点
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M >> S;
tree = vector<vector<u_int>>(N, vector<u_int>(0));
parent = vector<u_int>(N, 0);
depth = vector<u_int>(N, 0);
repeat(N - 1) {
u_int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
tree[x - 1].push_back(y);
tree[y - 1].push_back(x);
}
processTree(S, S, 1); // 根节点的父节点为自身,深度为 1
return 0;
}
有了树,接下来就好办了。 我们直接一个个上浮即可:
- C++
/* 省略部分代码 */
vector<u_int> ans(0);
int main() {
/* 省略部分代码 */
repeat(M) {
u_int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
until (depth[a - 1] == depth[b - 1]) {
if (depth[a - 1] > depth[b - 1]) a = parent[a - 1];
else b = parent[b - 1];
}
until (a == b) { // 比较 a 和 b
a = parent[a - 1];
b = parent[b - 1];
}
ans.push_back(a); // 此时 a/b 即为LCA
}
for (u_int& ancestor : ans) {
cout << ancestor << endl;
}
return 0;
}
当然,这种方法顶多拿个 90 分,
也不排除运气好直接满分的情况。
下面是完整代码:
- C++
/**
* 洛谷 P3379 解答程序。
* 使用 DFS 算法。
* @author CoolCLK
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define repeat(n) for (size_t _ = 0; _ < n; _++)
#define until(condition) while (!(condition))
typedef unsigned int u_int;
using namespace std;
vector<u_int> ans(0);
vector<vector<u_int>> tree;
vector<u_int> parent, depth;
u_int N, M, S;
void processTree(u_int __top, u_int __parent, u_int __depth) {
parent[__top - 1] = __parent; // 记录父节点
depth[__top - 1] = __depth; // 记录深度
for (auto& __node : tree[__top - 1]) {
if (__node == __parent) continue; // 避免回环
processTree(__node, __top, __depth + 1); // 递归处理子节点
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M >> S;
tree = vector<vector<u_int>>(N, vector<u_int>(0));
parent = vector<u_int>(N, 0);
depth = vector<u_int>(N, 0);
repeat(N - 1) {
u_int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
tree[x - 1].push_back(y);
tree[y - 1].push_back(x);
}
processTree(S, S, 1); // 根节点的父节点为自身,深度为 1
repeat(M) {
u_int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
until (depth[a - 1] == depth[b - 1]) {
if (depth[a - 1] > depth[b - 1]) a = parent[a - 1];
else b = parent[b - 1];
}
until (a == b) { // 比较 a 和 b
a = parent[a - 1];
b = parent[b - 1];
}
ans.push_back(a); // 此时 a/b 即为LCA
}
for (u_int& ancestor : ans) {
cout << ancestor << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 500005;
const int MAXLOG = 20;
vector<int> graph[MAXN];
int depth[MAXN], parent[MAXN][MAXLOG];
void dfs(int u, int p) {
depth[u] = depth[p] + 1;
parent[u][0] = p;
for (int i = 1; (1 << i) <= depth[u]; i++) {
parent[u][i] = parent[parent[u][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for (int v : graph[u]) {
if (v != p) dfs(v, u);
}
}
int lca(int u, int v) {
if (depth[u] < depth[v]) swap(u, v);
// 将u提升到与v同一深度
for (int i = MAXLOG - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (depth[u] - (1 << i) >= depth[v]) {
u = parent[u][i];
}
}
if (u == v) return u;
// 同时上提u和v
for (int i = MAXLOG - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (parent[u][i] != parent[v][i]) {
u = parent[u][i];
v = parent[v][i];
}
}
return parent[u][0];
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int N, M, S;
cin >> N >> M >> S;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
graph[x].push_back(y);
graph[y].push_back(x);
}
depth[0] = -1; // 深度基准
dfs(S, 0); // 从根节点开始DFS
while (M--) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << lca(a, b) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
- C++
- C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 500005;
struct Query {
int b, id;
};
vector<int> graph[MAXN];
vector<Query> queries[MAXN];
int parent[MAXN], ancestor[MAXN];
bool visited[MAXN];
int ans[MAXN];
int find(int x) {
if (ancestor[x] == x) return x;
return ancestor[x] = find(ancestor[x]);
}
void unite(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x != y) ancestor[y] = x;
}
void tarjan(int u) {
visited[u] = true;
ancestor[u] = u;
for (int v : graph[u]) {
if (visited[v]) continue;
tarjan(v);
unite(u, v);
ancestor[find(u)] = u;
}
for (const auto& q : queries[u]) {
if (visited[q.b]) {
ans[q.id] = find(q.b);
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int N, M, S;
cin >> N >> M >> S;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
graph[x].push_back(y);
graph[y].push_back(x);
}
// 存储查询
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
queries[a].push_back({b, i});
queries[b].push_back({a, i});
}
// 初始化并查集
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
ancestor[i] = i;
}
tarjan(S);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
cout << ans[i] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}